Links:
- semicon
Over time, piston oil seals may wear out or become damaged due to normal wear and tear, extreme temperatures, or poor maintenance practices. When this happens, oil leakage can occur, leading to decreased engine performance and potential damage to the engine.
In the world of industrial machinery, the significance of oil seals cannot be understated. These small but essential components play a crucial role in maintaining the efficiency and longevity of various types of equipment. An oil seal failure can lead to leaks, reduced performance, and even catastrophic machinery failure. Let's delve into the importance of oil seals, focusing on their composition, function, and the impact they have on industrial operations.
This tough, chemically inert polymer has a wide working scope as well as:
The metal case serves as the oil seal’s exterior or frame, providing rigidity and strength to the seal. The case material selection depends on the environment in which the seal will operate. Often, the same rubber material used in the seal element covers the case to help seal the exterior of the oil seal in the housing bore.
Choosing the right oil seal
In addition to these standardised types, the following special types are also available:
(type code)
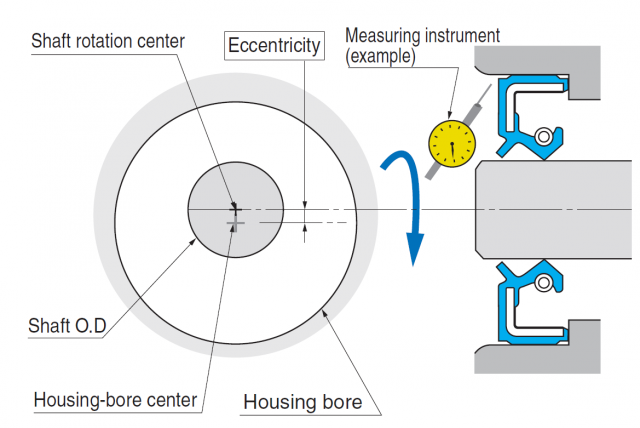
The best seal performance is achieved when close shaft and bore tolerances are present. Other factors include shaft eccentricity, end play and vibration.
Have you found the right oil seal for your application? The next step is fitting the oil seal correctly, so that it remains undamaged.
- Apply a small amount of gasket sealant or grease on the threads to facilitate installation and prevent leaks.
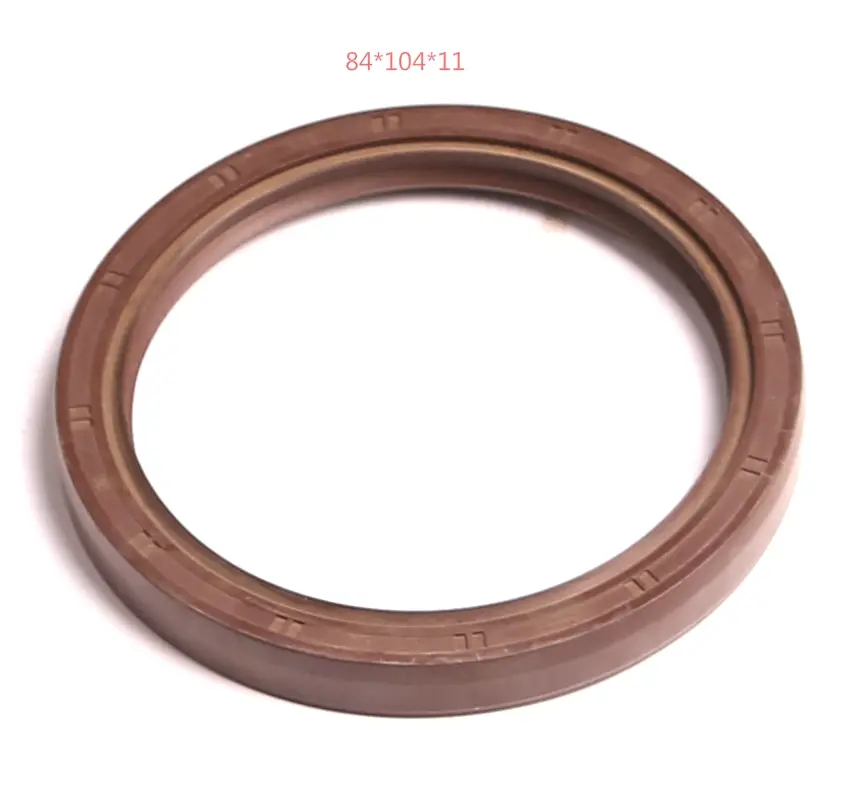 Conversely, a decrease in demand can lead to a surplus of oil seals, which can drive prices down Conversely, a decrease in demand can lead to a surplus of oil seals, which can drive prices down
Conversely, a decrease in demand can lead to a surplus of oil seals, which can drive prices down Conversely, a decrease in demand can lead to a surplus of oil seals, which can drive prices down oil seal price.
oil seal price. Rotary Wheel Of Auto Parts
Another type of seal design has the metal encased in rubber (Figure 2.11).
Mechanical seals are another type of oil seal that relies on mechanical components to create a seal